Hey soccer fans! Ever wondered how those split-second decisions about whether a goal was scored or not are made with such precision? Enter goal-line technology, the unsung hero of modern football. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the ins and outs of goal-line technology, from defining its working principles to discussing its cost, implementation in La Liga, and the rationale behind its introduction. So kick back, grab your favorite jersey, and let’s dive into the world of technology together!
What is Goal-Line Technology?

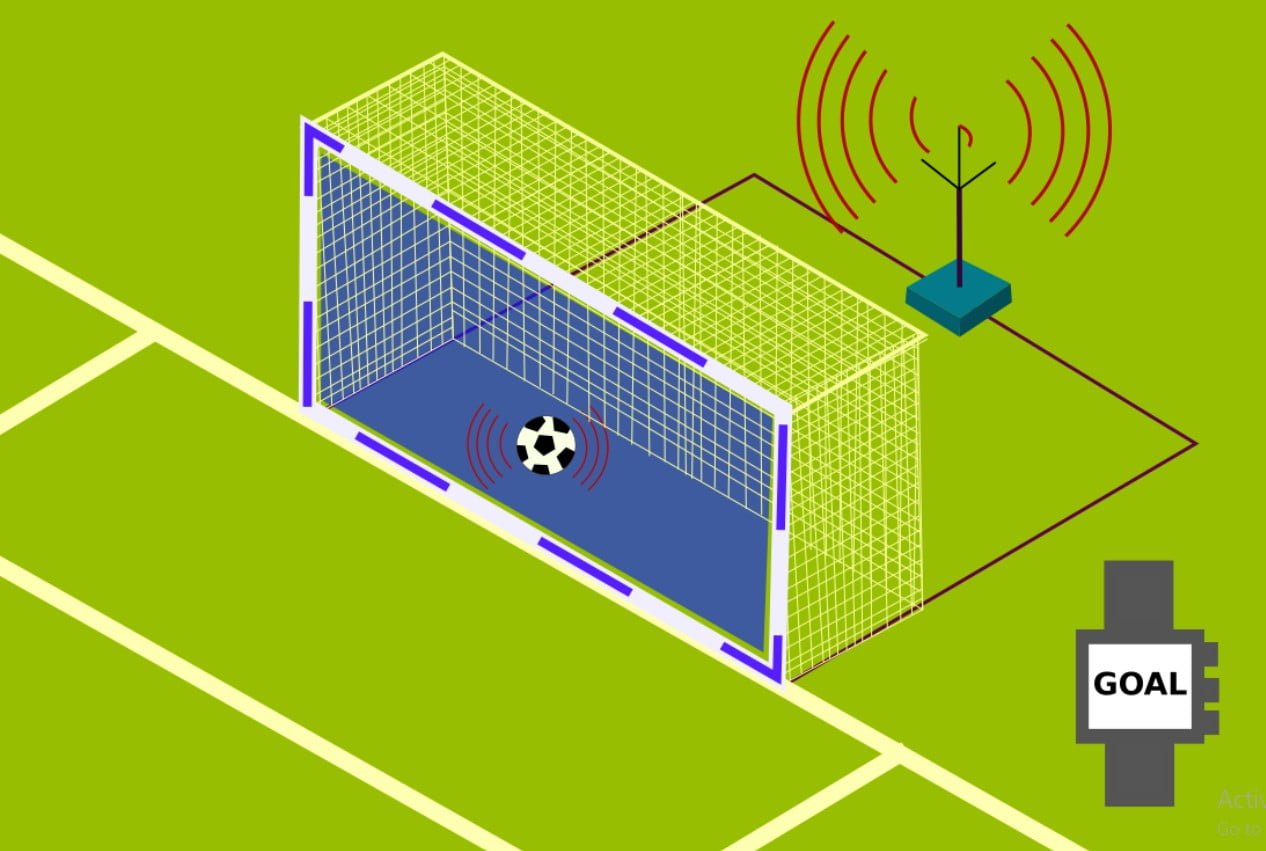
In football (soccer), goal-line technology (GLT) is an electronic system used to assess if the entire ball has crossed the goal line. This technology provides a conclusive answer in situations where there is doubt over whether the ball has crossed the goal line completely. It operates by strategically placing 14 high-speed cameras throughout the stadium to track the ball’s location in relation to the goal line. The system then processes data from these cameras in real-time to determine if the ball has crossed the line. If the system detects that the ball has fully crossed the goal line, it signals a goal.
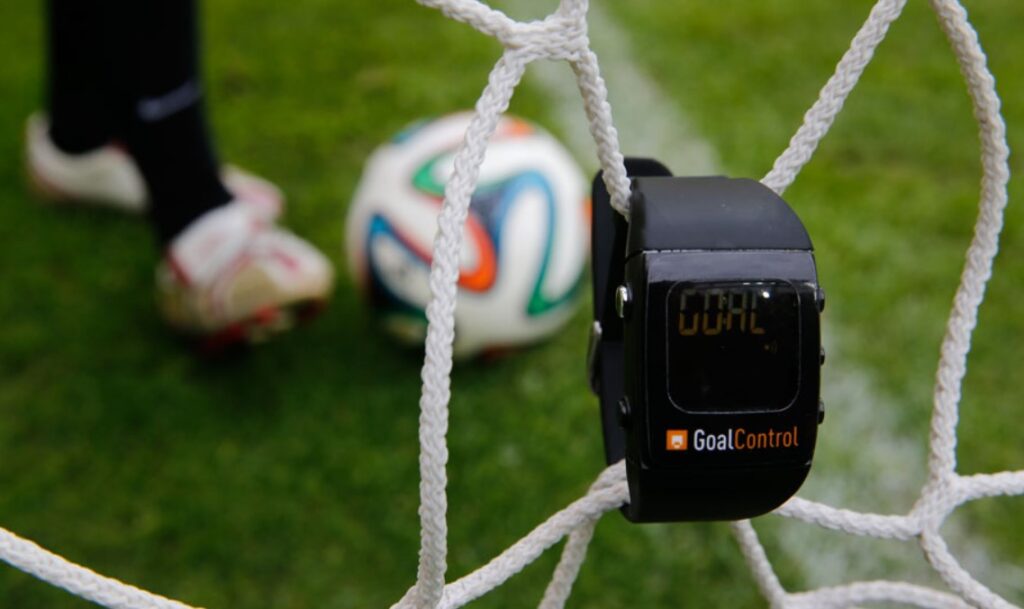
GLT is meant to be used in addition to match officials, not in place of them.If the ball does, in fact, cross the goal line, it sends a signal to the referee’s watch in less than a second, allowing for quick decision-making. Since its official approval by the International Football Association Board (IFAB) in 2012, GLT has been included in major tournaments such as the FIFA World Cup since 2014. GLT’s implementation has significantly improved the accuracy of goal decisions in football matches. Ultimately, Goal-Line Technology promotes fair play and facilitates quick decision-making at crucial moments in the game.
Its main purpose is to help referees make correct calls in situations where it can be difficult to determine if the ball has crossed the goal line completely. GLT provides instant and accurate feedback to referees, ensuring fair play and reducing controversies. Its implementation has significantly improved the accuracy of goal decisions in football matches. Goal-Line Technology ultimately promotes fair play and facilitates quick decision-making at crucial moments in the game.
Neil Warnock
I’m glad to see goal-line technology working; we should have had it for years. I do believe we will soon see managers being allowed one, or two, challenges.
History of Goal-line Technology
Before 2011, the Premier League began working with Hawk-Eye in 2006 to investigate camera-based technologies that could improve football decision-making. The 2006–07 season saw the first trials held at Craven Cottage Stadium, home of Fulham.

FIFA’s Position and Turning Point
In March 2008, the International Football Association Board (IFAB) rejected the idea of using technology in football, despite some early successes. However, the infamous event during the 2010 FIFA World Cup, where Frank Lampard’s strike crossed the goal line but was not recognized, caused FIFA to change its mind. This event catalyzed reconsidering the use of technology to assist referees in making accurate decisions during matches. As a result, IFAB eventually approved the implementation of goal-line technology in football. Sepp Blatter, the president of FIFA, suggested reevaluating the use of GLT.
Official Approval and Integration
In July 2012, the IFAB officially approved the adoption of GLT after extensive testing in England, Germany, Hungary, and Italy. The first two systems to pass testing and obtain FIFA goalline technology licenses were Hawk-Eye and GoalRef.
Adoption of Hawk-Eye
The Premier League chose Hawk-Eye as their GLT provider beginning in the 2013–14 season, originally known as the Goal Decision System (GDS). Hawk-Eye is a technology that was first created for tennis and cricket. It uses cameras to track the trajectory of the ball and make accurate decisions.
Why was it Introduced and its purpose?
Do you recall the World Cup of 2010? When England was denied a clear goal against Germany, everyone finally said, “Enough is enough.” The introduction of goal-line technology ensures that this does not occur again. Maintaining the integrity of the game is crucial.
The principal aim of goal-line technology (GLT) is to provide a conclusive and accurate determination of whether a football has crossed the goal line entirely. This is a critical aspect in establishing the legitimacy of a goal. Referees benefit from this technology’s objectivity as it provides concrete evidence. This is especially valuable in fast-paced matches where human judgment may not be able to appropriately analyze such occurrences. This technology enhances the accuracy and fairness of decision-making on goal-related incidents, ultimately ensuring a fair outcome for both teams. Additionally, it helps maintain the integrity of the game by minimizing disputes and controversies surrounding goal decisions.
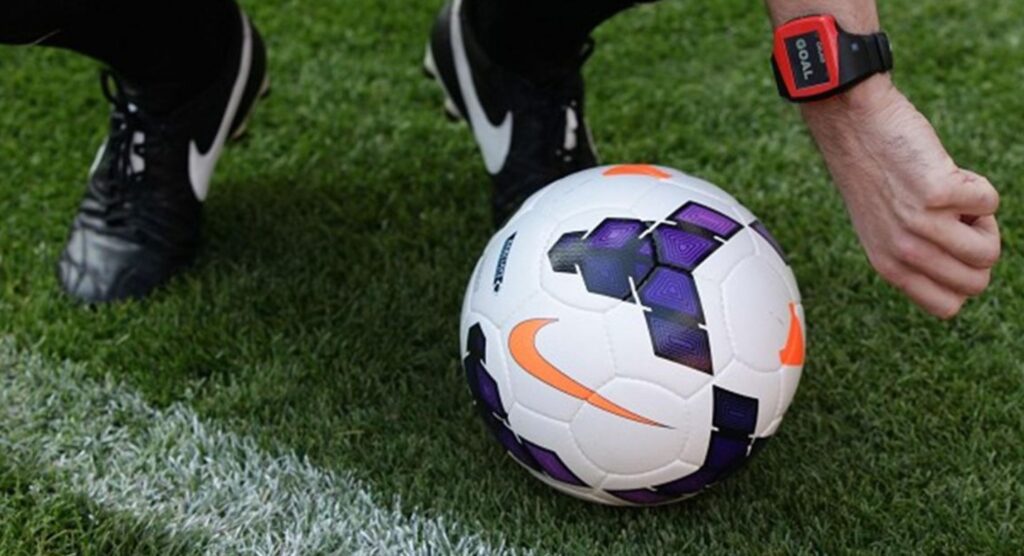

By using advanced magnetic field systems or high-speed cameras connected to computers, GLT systems may instantly send data to the referee’s watch. This removes any doubt about goal-scoring determinations. This technology’s implementation attempts to improve football’s fairness and reduce controversy. It especially aims to address high-profile events when bad goal calls affect the outcome of games.
It is important to stress that GLT is intended to supplement official decision-making, not to take the place of it. The goal of the technology is to provide clear confirmation of whether the ball has crossed the line. This will help referees make their final decision. Elite domestic leagues adopted this technique in July 2012 after the International Football Association Board (IFAB) approved it.
How Does it Work?
Imagine a bunch of cameras or sensors around the goal, all working together like detectives on a case. They track the ball’s position and send the info to the referee’s watch faster than you can say “GOAL!” If the entire ball crosses the line, the ref gets a buzz, and it’s time to celebrate! In football, this technology serves as an essential tool that facilitates the decision-making process regarding whether the ball has fully crossed the goal line and should be counted as a goal.
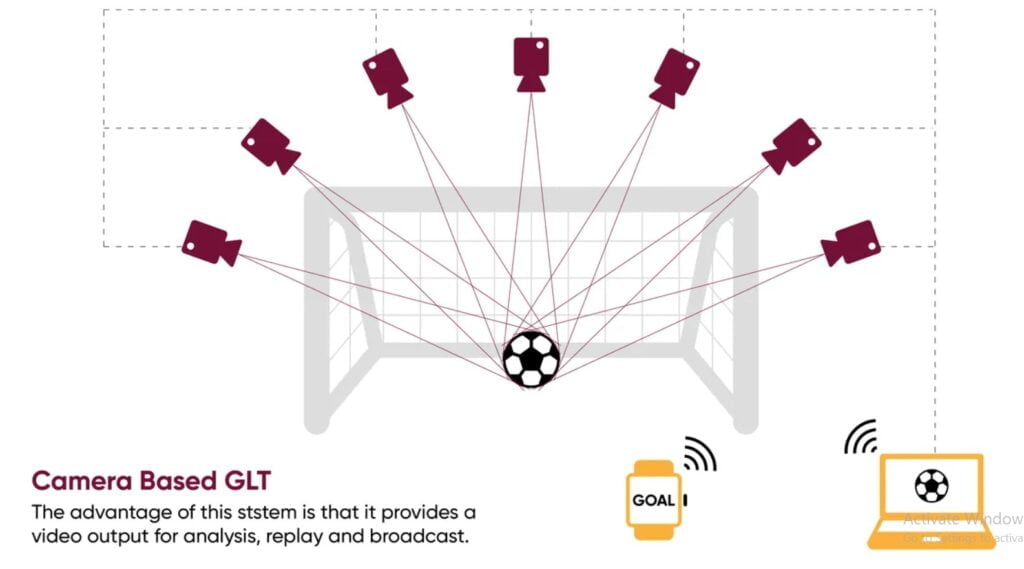
Camera-Based Systems
Systems like Hawk-Eye utilize several strategically positioned high-speed cameras throughout the stadium to track the location of the ball. These cameras provide a three-dimensional image that shows the exact location of the ball. If the ball crosses the goal line completely, the system sends an encrypted signal to the referee’s watch in less than a second.
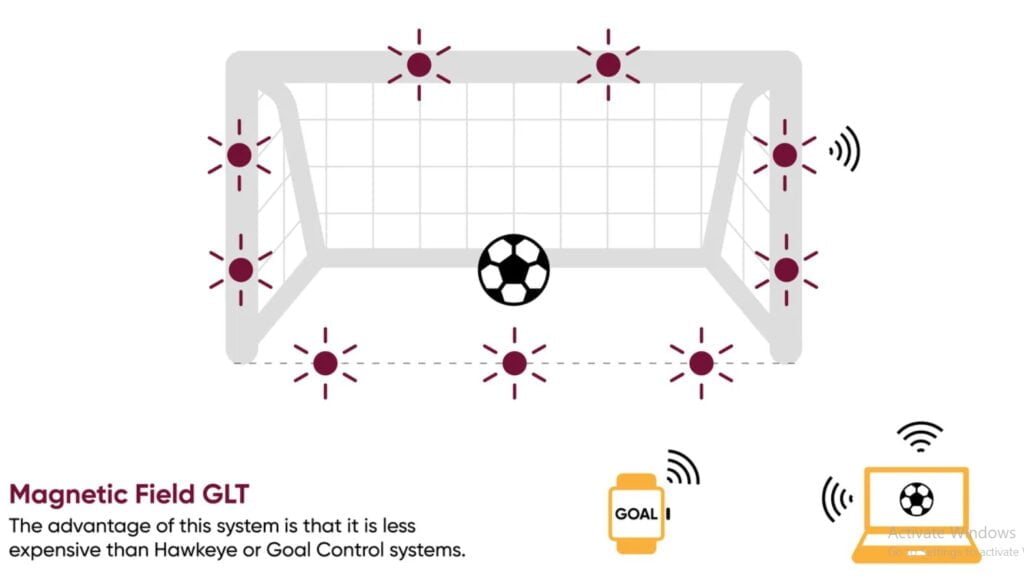
Magnetic Field Systems
Using a magnetic field that surrounds the target region is an alternate technique. When a ball with a sensor crosses the goal line and breaks the magnetic field, the referee’s watch immediately receives a signal indicating a goal. Before every match, thorough testing of the system ensures correct calibration. Since its introduction in 2014, it has become an essential component of football. It aids referees in making prompt and accurate calls throughout the play.
The Cost Factor
In football, goal-line technology is a crucial element that provides accurate assessments of whether the ball has passed the goal line. Nonetheless, organizations and stadiums must take the cost of deploying this technology into serious account. However, its installation may be quite expensive, costing an average of $260,000 per stadium. Additionally, the cost of operations is about $3,900 for each game. These prices could change based on the particular technology used and the particular needs of any venue.
The technology usually consists of magnetic field devices or high-speed cameras that provide match officials with real-time input. Even though it costs more upfront, the improved fairness and precision it gives the game are seen as priceless benefits. However, the financial consequences are still up for debate, especially for smaller leagues and teams where the cost of such an investment would be prohibitive.
It’s important to note that these expenses balance against the potential consequences of incorrect goal calls on game results. Such errors can significantly impact professional football. Future developments in technology could make it possible to lower costs. This could also lead to wider implementation of the technology at different levels of the sport.
Examples of Goal-Line Technology in Action
Let’s take a look at some memorable examples in action:
- FIFA World Cup: Goal-line technology made its debut in the FIFA World Cup during the 2014 tournament held in Brazil. One notable instance occurred during a match between France and Honduras, where the technology confirmed Karim Benzema’s goal.
- Premier League: The English Premier League adopted this technique in the 2013-2014 season. Since then, it has been instrumental in resolving contentious goal decisions and maintaining the integrity of the competition.
- UEFA Champions League: Europe’s premier club competition, the UEFA Champions League, implemented this technique to ensure accurate and fair officiating during critical matches.
Interesting Facts About Goal Line
Goal-line technology has undergone significant evolution, transitioning from early experiments to sophisticated camera and magnetic field systems.
– Hawk-Eye, a key provider of this type of technology, originally gained prominence in tennis and cricket before expanding to football.
– One of the remarkable features of goal-line technology is its ability to provide instant feedback to referees, allowing for immediate goal decisions.
– It made its FIFA World Cup debut during the 2014 tournament in Brazil, marking a historic moment in football officiating.
– Despite its benefits, implementing goal-line technology entails substantial costs for stadiums and leagues.
– The success of this technique in football has spurred discussions about its potential application in other sports facing similar challenges.
– Beyond practical benefits, goal-line technology plays a vital role in upholding the fairness and integrity of the game by providing objective evidence in goal-scoring situations.
Recommended Reads
Facts About Electricity | Electrifying Facts
Facts About Technology | Facts That Point To The Future
Technical Facts | Technological Marvels Unveiled
Future of Goal-line Technology
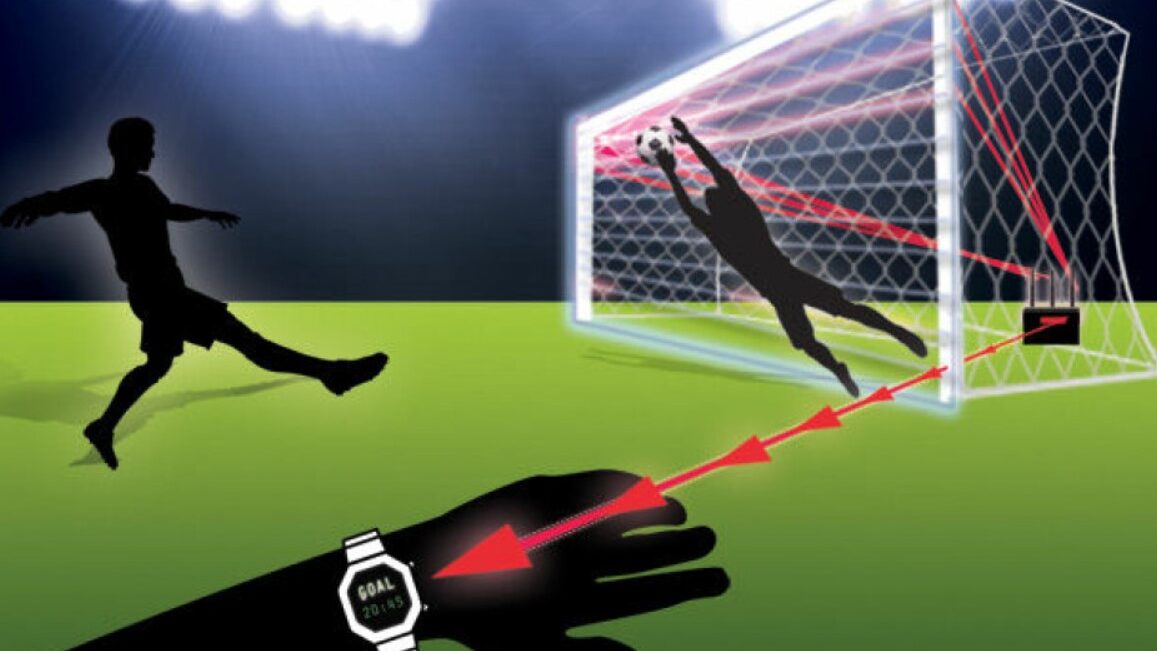
Goal-line technology has a bright future ahead of it and is expected to develop in step with other technical advancements. Goal-line technology is now an essential component of football, providing a conclusive means of establishing whether the ball has crossed the goal line in its entirety. It works by using magnetic field devices or high-speed cameras to quickly transmit data to the referee’s watch, which guarantees accurate and timely decision-making throughout games.
In the future, we may expect more improvements to improve the precision and speed of the system. Prospective advancements might involve incorporating additional technologies, such as partially automated offside technology, which could further simplify the process of making decisions. Furthermore, goal-line technology’s extensive use in football may open the door for its use in other sports facing comparable difficulties with score or point adjudication.
Goal-line technology has transformed football since its introduction, and new developments indicate that it is becoming increasingly important. It will become more and more essential as improvements continue, supporting equity and reducing the controversy around goal-scoring occurrences.
Final Words
Goal-line technology is an acknowledgment that football values fairness and precision more than it is merely a nice device. Thus, keep in mind that goal-line technology has your back the next time you’re chewing your fingernails during a game! With goal-line technology, you can now enjoy a game or two with the assurance that every goal will be scored fairly. I appreciate clear objectives and even more clear regulations.
FAQ’s
La Liga, Spain’s top football league, has chosen not to adopt goal-line technology due to high costs, making it the only major European league without it. This decision has sparked controversy, especially after disputed goals in matches like El Clásico. Without goal-line technology, match officials must rely solely on their judgment. They determine if the ball has crossed the goal line.
FIFA World Cup 2014: Debut in Brazil confirmed Karim Benzema’s goal for France against Honduras.
Premier League: Implemented in 2013-2014, resolving goal controversies.
UEFA Champions League: Ensures accurate officiating in key matches.
No, goal-line technology is not part of VAR. Different purposes in football require separate systems. Moreover, goal-line technology solely determines whether the ball has crossed the goal line, while VAR reviews various decisions made by match officials.
Goal-line technology includes camera-based and magnetic field systems, along with referee watches. Cameras monitor the ball’s position, while magnetic fields track its movement. Referees receive immediate signals on their watches to make accurate decisions. These components ensure quick and reliable determinations during matches.